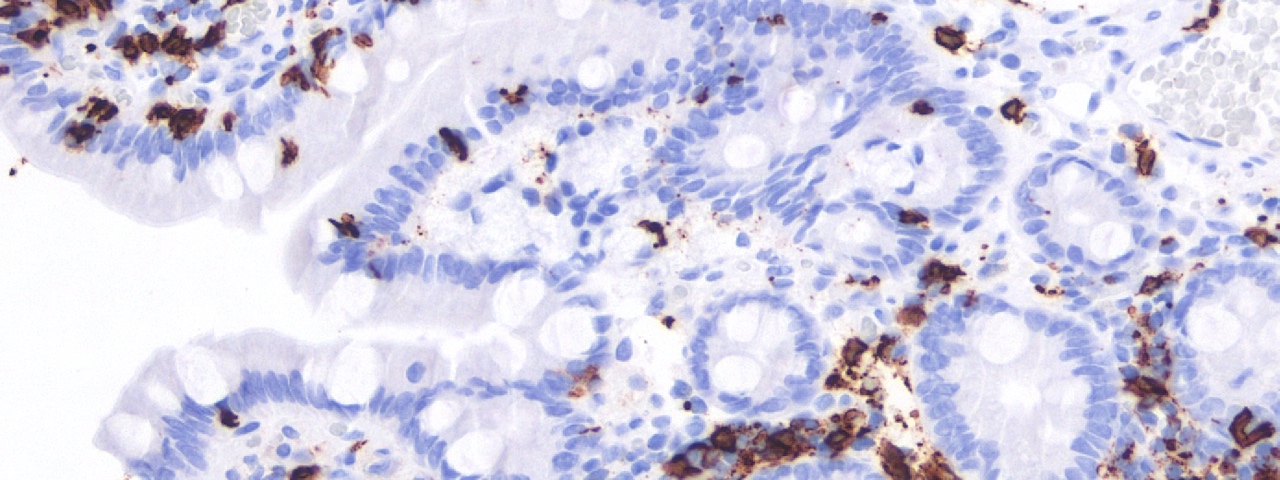
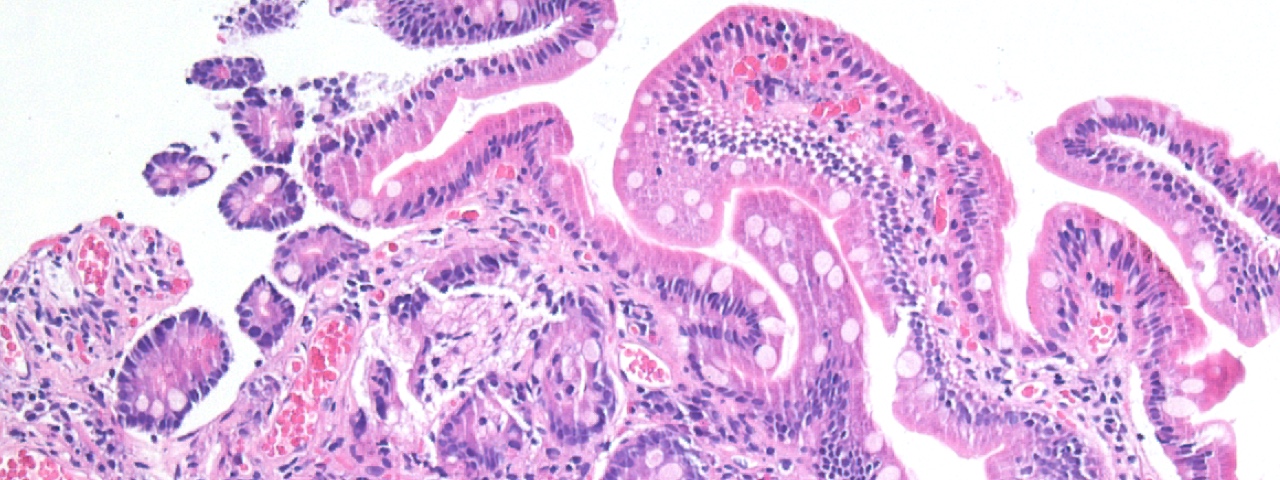
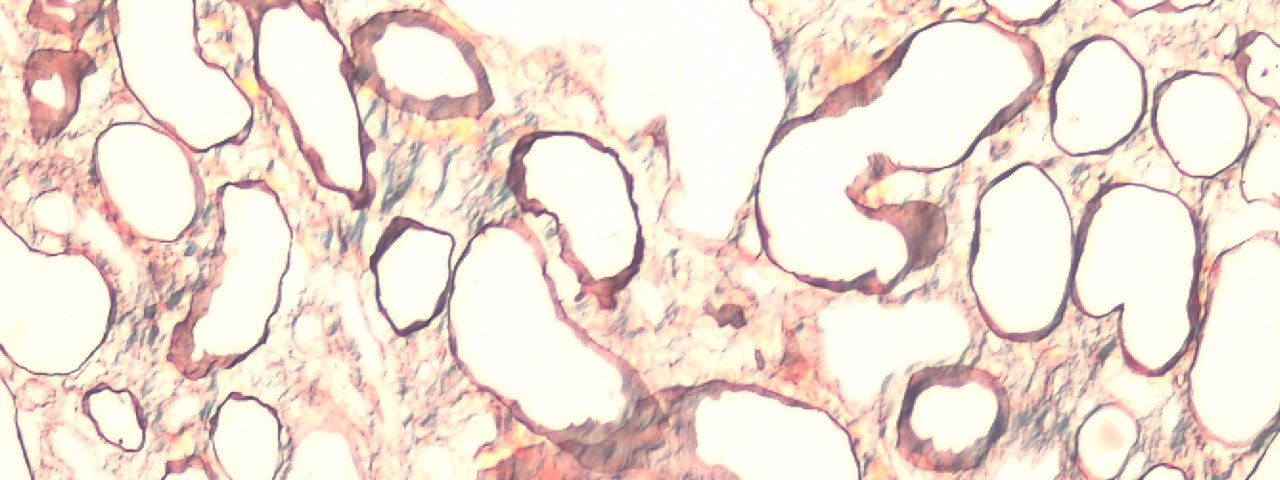
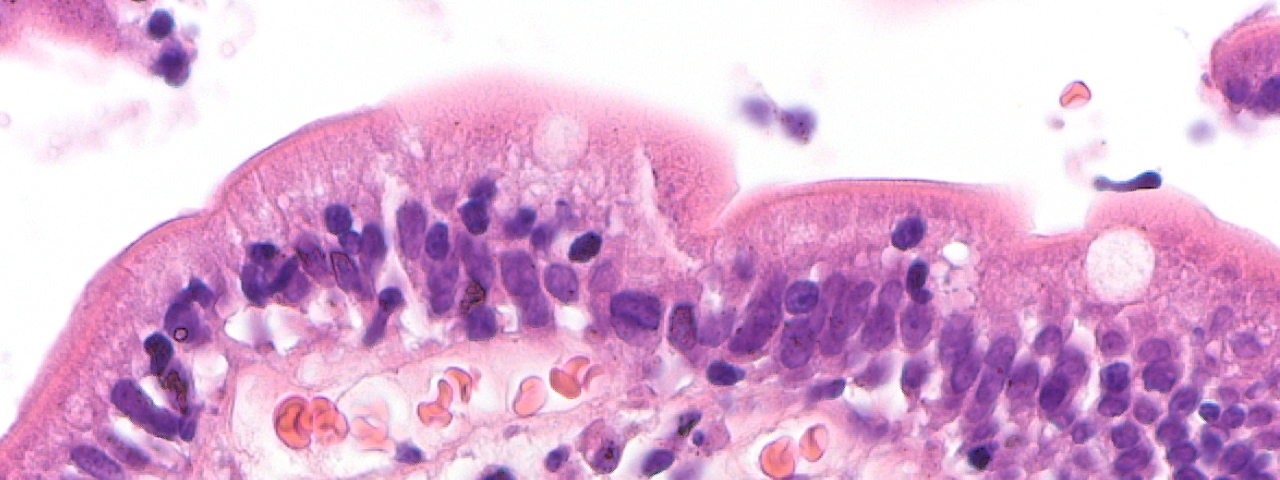
The goal of the CRC 1160
The Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1160. “Immune-mediated pathology as a consequence of impaired immune reactions (IMPATH)” is a research consortium of clinical and basic immunologists exploring the basis of diseases mediated by the immune system.
The CRC sets out to challenge the traditional idea that an “overreaction” or “deviation“ of normal immune responses is pivotal to immune mediated pathology and that, consequently, immunosuppression is the appropriate therapeutic strategy for such disorders. Instead, the conceptual basis of the CRC is the idea that impaired immune reactions constitute a major prerequisite for immunopathology. This is what we call the “IMPATH paradox”. This paradox implies that immune reconstitution and/or immune stimulation rather than immunosuppression represent appropriate therapeutic principles for these forms of immunopathology.
News
Publications
Runge S, von Zedtwitz S, Maucher AM, Bruno P, Osbelt L, Zhao B, Gernand AM, Lesker TR, Gräwe K, Rogg M, Schell C, Boerries M, Strowig T, Andrieux G, Hild B, Rosshart SP. 2025. Laboratory mice engrafted with natural gut microbiota possess a wildling-like phenotype. Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 12;16(1):5301. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60554-2.
Giesler S, Biavasco F, Wertheimer T, Zeiser R, Vinnakota JM. 2025. Biology-driven therapies of CAR T immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome. Immunotherapy. 29:1-11. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2510893.
Grimmeisen M, Wang X, Weldle M, Sartory K, Benkhelifa S, Zhang Y, Dao T, Meyer J, Gorka O, Groß O, Jessen-Trefzer C. 2025. Synthesis and Evaluation of Trehalose-Based Mertansine Warheads for BCG Delivery of Anti-Cancer Agents. Chembiochem. 2025 May 27:e202500390. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500390.
Sankowski R, Prinz M. 2025. A dynamic and multimodal framework to define microglial states. Nat Neurosci. 2025 May 20. doi: 10.1038/s41593-025-01978-3.
Teng YH, Appiah B, Andrieux G, Schrempp M, Rose K, Hofmann AS, Ku M, Beyes S, Boerries M, Hecht A. 2025. TGF-β signaling redirects Sox11 gene regulatory activity to promote partial EMT and collective invasion of oncogenically transformed intestinal organoids. Oncogenesis. 2025 May 20;14(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41389-025-00560-7